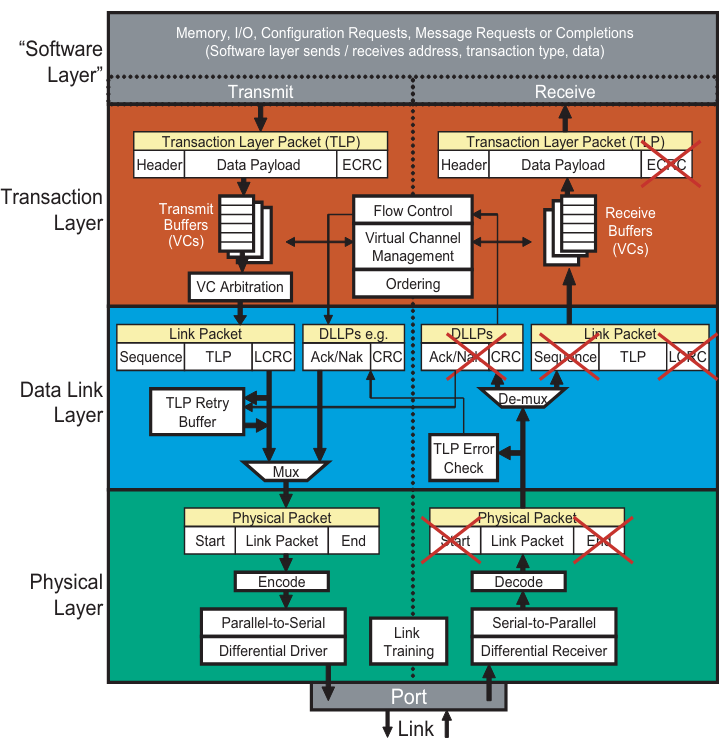
1️⃣ Packet Creation in Transaction Layer
-
Input: Device core presents:
- Command type (read, write, completion, message)
- Address
- Attributes (priority, ordering, etc.)
-
Transaction Layer does:
- Builds a Transaction Layer Packet (TLP).
- Stores it in a Virtual Channel buffer (essentially a queue).
- Waits until flow control says there’s space on the link.
2️⃣ Data Link Layer Adds Reliability
- Adds:
- Sequence number
- LCRC (Link CRC) for error checking
- Keeps a copy of the packet so it can resend if the receiver NAKs (negative acknowledge).
- Passes the packet down to the Physical Layer once ready.
3️⃣ Physical Layer Encodes & Transmits
- Encodes packet (8b/10b or 128b/130b).
- Scrambles data to ensure good signal integrity.
- Serializes and sends bits across all available lanes using differential signaling.
- Link Training (done earlier) guarantees both sides agree on speed and width.
4️⃣ Reception – The Reverse Process
When the other side receives:
-
Physical Layer
- Recovers clock using CDR (Clock and Data Recovery).
- Deserializes bitstream → parallel data.
- Decodes 8b/10b or 128b/130b.
- Passes up to DLL.
-
Data Link Layer
- Checks LCRC, sequence numbers.
- If good → sends Ack back.
- If bad → requests retransmission (Nak).
- Forwards to TL if valid.
-
Transaction Layer
-
Buffers packet, extracts:
- Command
- Address
- Attributes
-
Passes to device core (or switch routing logic).
-
If this is a switch → creates a new TLP for the outgoing port.
-
🧠 Big Picture: Layer-to-Layer Communication
-
Upper layers talk in terms of packets.
- TL → organizes data into TLPs.
- DLL → wraps them with reliability info (DLLPs).
- PL → just moves bits reliably, doesn’t “understand” the content.
-
Each layer only talks to its peer on the other side.
- TL on one side ↔ TL on the other.
- DLL ↔ DLL.
- PL ↔ PL.
💡 Why This Matters
- Ensures modularity: Each link segment has its own error detection/retransmit, so errors are handled locally (no need to resend across the entire chain).
- Makes switches work: Since each port terminates a link, it must fully decode/encode packets before forwarding.
- Allows concurrent traffic: Different links can operate independently, each with its own flow control